Before you'll start to read the HRM essay sample from our professional writers, remember that if you need someone to write your human resource management paper - ask for help from our HRM paper writing service. Just fill in all your paper requirements and our professional HRM writers will do the rest!
Introduction
Human Resource Management (HRM) and Personnel Management (PM) are crucial aspects of management that provide such functions as recruitment, selection, training, and learning of the employees. HRM, as well as PM, refers to managing people at work. Consequently, one should study them to understand their functions and operations. There are differences between HRM and PM that are related to the type of organization and key operations. One should say that the proper application of both practices can contribute to the company. As a result, the current paper intends to provide an understanding of HRM, its role, and functions related to the legislation, development, reward, and resourcing.
Organizational Structure and Culture
LO 1. Understanding the Relationship between Organizational Structure and Culture
1. 1. Distinguishing between Personnel Management and Human Resource Management
There are crucial differences between PM and HRM. PM approach is a traditional way of managing people. As to HRM, it is more modern and innovative. As a result, it is more typical for larger organizations. PM pays more attention to labor relations, employee welfare, and personnel administration than to the development of human resources. As to HRM, it has a wider variety of functions that include maintenance of human resources, motivation, development, and acquisition. PM regards people as a way of achieving the desired results. For HRM, people are the most valuable and important resources for fulfilling goals (Armstrong & Taylor 2014).
Another difference refers to the function of both aspects of management. PM addresses the employee's satisfaction. HRM has an administrative function that is more strategic and effective. One should say that the division of labor is typical for PM. As to HRM, its key principle is to use teamwork that presupposes more creativity. The weakness of PM is that it does not provide much training and learning. HRM opens more training and developing opportunities (Barrick & Zimmerman 2009). Consequently, HRM is more actual and modern in the present conditions of business.
1.2. The Assessment of the Function of HRM in Contributing to Organisational Purposes
The key function of HRM is managing people that is based on the following operations: compliance with employment legislation, employee relations, performance appraisal, reward system, training and development, selection, and recruitment. All of the given operations contribute to organizational purposes. Recruitment and selection are critical to organizational performance as the proper selecting of employees can increase the company's productivity. Training and development benefit organizational contributions, employees' knowledge, loyalty, and return on investments. It is crucial to follow the employment legislations that include Employment Relation Act 2004, the Race Relation Act, Disability Discrimination Act 1995, and Equal Pay Acts 1970 and 1983 (Beebe, et al. 2013).
The employee relation is another aspect that contributes to organizational purposes. First, it creates a friendly and favorable atmosphere. Second, it increases motivation, productivity, and encourages creativity. Performance appraisal should be systemic to promote employees to work better. Performance appraisal can be done through promotion, communication, compensation, and employee development. The reward system can include high salary rates, bonuses, extra benefits, and insurance packages (Berman, et al. 2010). All such operations contribute to the place of the company in the market, its competitive advantage, and financial growth.
1.3. Evaluation of the Role and Responsibilities of Line Managers in HRM
The role and responsibilities of line managers in HRM are diverse. They include HR planning, retention, induction, selection, recruitment, resolution of conflicts, handling grievances, performance appraisal, termination of employment, compliance with all employment legislation, encouragement of employees, demonstrating good leadership, and promotion of sound industrial relations. HR planning is an essential aspect of line managers' work. HR planning includes all factors related to HRM and allows fulfilling all tasks in time. Moreover, it presupposes engaging all employees to the fullest extent. Retention of employees is based on dealing with them, suggesting performance appraisal, their encouragement, and handling grievances (Brown 2012).
Induction is a good method regarding the selection and recruitment processes. It helps ensure that the company employs the necessary, productive, and creative staff. Moreover, line managers in HRM should demonstrate successful leadership proving that indifference and improper attitude to the work may have negative consequences. Consequently, all employment legislation should become managers' instructions for managing human resources. Moreover, line managers should promote sound industrial relationships and resolve conflicts in time to improve the organizational reputation (Chen & Huang 2009).
1.4. The Analysis of the Impact of the Legal and Regulatory Framework on Human Resource Management
The legal and regulatory framework regarding HRM deals with many laws and regulations that coordinate the smooth relationships between employers and employees. It means that such legislations forbid discrimination and guarantee safe working conditions. For example, the Equal Pay Act 1970 does not allow discrimination in employment-related to financial points and gender differences. National Minimum Wage Rate Act 1998 states that every employee should receive a minimum salary per hour. Employment Rights Act 1996 states that recruitment and selection processes should be fair to diverse people. Rehabilitation of Offender Act (1974) coordinates that an employer ignores criminal convictions and gives the chance to workers (Gibb 2011).
Work and Families Act (2006) helps employees to protect their family rights at work without any serious issues. The act guarantees flexible working times, paternity leaves, maternity leaves, and payments. Employment Act (2008) regulates the relationships between employers and employees, especially when there are disputes between them. Disability Discrimination Act (1995 with amendments in 2005) prohibits the discrimination of employees with disabilities (Gibb 2011). The rights of employees are protected by legal regulations.
LO2. Understanding Different Approaches to Management and Leadership
2.1. The Reasons for Human Resource Planning in Organizations
HR planning is a systematic evaluation of HR demands and the necessity of employees with the required knowledge and skills. Consequently, HR planning concerns retirement services, career development, training, and recruiting. HR planning presupposes making conclusions, goals, creating objectives, and collecting information. The key objectives for HR planning are to analyze the number and productivity of employees, determine what kind of employees the company has and should have for better performance. Another task of HR planning is to monitor the available resources of the organization and to maintain the employees. HR planning will bring organizational progress and become an essential part of the management information system (Harzing & Pinnington 2010).
HR planning includes forecasting future manpower needs that help predict the necessity of human resources. Any company needs changes, and only HR planning will benefit from coping with any changes. Moreover, recruiting talented people is a long process that demands careful planning and analysis. As a result, HR planning is an extremely necessary process as it can reconstruct work processes, cope with redundancy and retirement, and identify training needs.
Our Features
2.2. The Stages Involved in Planning HR Requirements
One can distinguish the following stages for planning HR requirements: beginning with organizational objectives and plans, scanning the external environment, analysis of the employee's skills and potentials, forecasting of organizational needs and supply of the available people, comparison, making adjustments for expansion, contraction, and remaining the same. However, the essential process is the analysis and assessment of the current human resources as the current stage helps determine whether the company needs the new ones. Another most crucial stage is forecasting HR requirements to understand how many resources the company should recruit to achieve the organizational objectives and predict the changes shortly (Harzing 2010).
Gap analysis is also inevitable as it helps determine what new jobs the organization needs, what skills it requires to become more productive, and understand whether all employees have the required skills and knowledge. It is not less important to develop HR strategies to support the company's goals and mission. First, one should restructure strategies, develop training, development, and collaboration methods. Second, one should match demand and supply to forecast the supply of labor and actual needs in it.
2.3. The Comparison of the Recruitment and Selection Process in Two Organizations
One should analyze the recruitment and selection process of TESCO UK and ASDA. TESCO has more complicated procedures that include identification of vacancies, development of the position, development of recruitment plan, implementation of the recruitment plan, conducting interviews, and finalizing recruitment. As TESCO is a large company it has more job vacancies. First, TESCO advertises its vacancies on the site and screens the applicant's CVs. Second, TESCO invites the most successful candidates for interviewing and sends letters to not unsuitable applicants. Third, the company has the second interview to be sure that the candidates will be beneficial for them.
ASDA uses similar techniques for recruitment and selection processes. However, their procedure is more simplified. It includes the following steps: job analysis, job description, the attraction of the applicants, selection, and induction. The process of recruitment and selection of the company differs from the Tescos one. First, ASDA does not send e-mails to the candidates that failed the interview. Moreover, their induction is four weeks. It means that ASDA needs more time for analysis of the interviewing results.
2.4. The Effectiveness of the Recruitment and Selection Techniques in Two Organizations
One can say that the recruitment and selection techniques in TESCO and ASDA are effective as they are complex. However, the recruitment and selection process of TESCO is more developed than in ASDA. Consequently, it is more beneficial. The advantage of the recruitment and selection techniques in TESCO is that they are more attentive to their applicants as most companies do not inform about the negative results, such as ASDA. The disadvantage of the recruitment techniques of TESCO refers to the inability to control all human resources and vacancies. Moreover, the company should always improve its techniques due to the emergence of new jobs and employees.
The advantage of the recruitment and selection techniques of ASDA is that it is a smaller organization than TESCO and it can implement a stable combination of techniques to provide a fair selection process. The disadvantage of ASDAs selection techniques is that the company is not very attentive to its applicants. Moreover, the process of recruitment is more simplified. As a result, it omits the second interviewing that is necessary to ensure the rightness of the choice.
LO3. Understanding Ways of Using Motivational Theories in Organizations
3.1. The Assessment of the Link between Motivational Theory and Reward
There is a link between motivational theory and reward. If people are rewarded for their work they are motivated to work harder to satisfy their expectations and needs. Motivation is the process when people are striving for increasing their productivity and performance. One can distinguish the following motivational factors: career promotion, personal growth, benefits, and bonuses. Motivation can influence other people and achieve goals and objectives. Consequently, HR managers should reward their employees to increase productivity and make them highly motivated. However, the reward depends on the quality of the employee's work and his/her desire to help the company (Findler, et al. 2007).
The key motivational theory is Maslow's hierarchy of needs that satisfies physiological needs, safety and security, love and belonging, self-esteem, and self-actualization. Managers who follow such a theory can encourage employees to do more attractive work and more rewards for them. Consequently, every company should develop its reward system to be unique and attract more customers. The reward should be financial (bonuses, payments) and non-financial (promotion, learning, development) to motivate the employees.
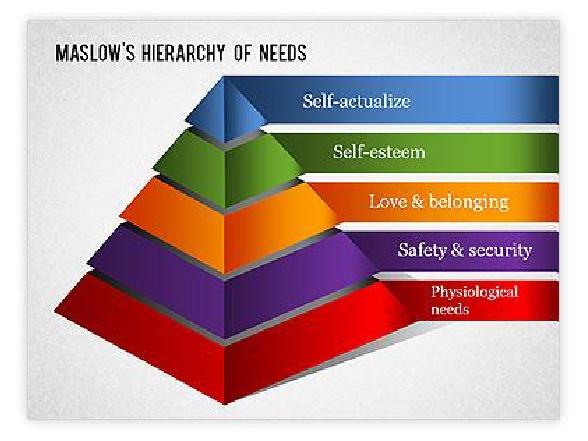
Figure. Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
3.2. The Evaluation of the Process of Job Evaluation and Other Factors Determining Pay
To assess the process of job evaluation, one should use analytical and non-analytical methods. Non-analytical methods are designed based on the jobs presented in the company. They are a ranking method and classification method. The analytical methods are based on the requirements of the job. They are point method and factor comparison. Skills, qualifications of the employee, knowledge, and competence are the factors determining pay. The outcome of the job evaluation can become the decision for changes of duties and responsibilities of the employee, redesigning the jobs, improvement of job design, and fair salary payments (Klarsfed 2010).






The level of responsibility, occupational hazards, and environmental conditions are also influential for the payment. It is evident that if the work threatens the health and safety of the employee, it should be highly paid. Moreover, one can refer to such factors determining pay as employee performance, the profitability of the organization, industry sector, skills, experience, seniority, and size of the organization. HR managers should take into consideration employee perception of wage, government regulations, and cost of living to be fair in determining the payment (Chen & Huang 2009).
3.3. The assessment of the Effectiveness of Reward Systems in Different Contexts
One can distinguish the extrinsic rewards and intrinsic rewards. They are applied according to the type of context. The extrinsic rewards include target bonuses, commissions, gifts, salary increments, paid sick leave, paternity and maternity leave, and bonuses. The intrinsic rewards include authority, more responsibilities, trust, seniority, promotions, recognition, praise, and good feedback. Small organizations are less profitable. Consequently, intrinsic rewards are more acceptable for them. Large organizations have enough profits and resources to provide extrinsic, as well as intrinsic rewards. Moreover, the companies that are more experienced in the market are more flexible in the choice of rewards as they understand that it will benefit them (Findler, et al. 2007).
The more profitable the company is, the more extrinsic rewards it can provide. The companies of the public sector tend to use good feedbacks, and more responsibilities as bonuses and commissions are not available for them due to the lack of human resources. Moreover, the rewards depend on the nature of the job as the harder work is, the more paying it should be (Stone 2013).
3.4. The Methods for Monitoring Employee Performance
One can distinguish the following methods for monitoring employee performance: performance reviews, customer feedbacks, dashboards, and peer appraisals. Performance reviews allow managers to track employees' progression and fulfillment. Moreover, such performance reviews allow fulfillment rating of performance. A performance review sheet can include customer complaints, error rates, and other factors related to performance. Peer appraisal is another technique that is recorded as a valuable resource of information. One should say that every employee has his/her opinion about co-workers' performance. However, one should say that peer appraisals can be subjective. Consequently, HR managers should observe for productivity and performance of employees themselves (Klarsfeld 2010).
One recommends using dashboards to track performance. They include a variety of metrics, such as error rates, defect rates, and other violations. However, one should say that customer feedbacks are the most objective technique for monitoring employee performance. HR managers should track employee complaints as the basis for quality assurance (Pinto & Pinto 2011). One recommends combining the methods for monitoring employee performance to receive the objective results.
Great Academic Papers Writing Service
LO4. Understanding Mechanisms for Developing Effective Teamwork in Organizations
4.1. The Reasons for Cessation of Employment with an Organization
Cessation of employment is an employee leaving the organization for personal reasons or terminating the employment for other reasons. The reasons for cessation of employment are the following: dissatisfaction with work and its conditions, poor relationships with the boss, negative relationships with co-workers, and lack of opportunities to use abilities and skills. Moreover, employees can leave their work because they feel underestimated and cannot contribute to the business goals. They can cease employment as they do not have independence and autonomy in their actions and decisions. Moreover, the meaningfulness of a job can also lead to the cessation of employment.
Most employees leave their jobs because their performance is not recognized by managers. The overall corporate culture of the company can also be dissatisfactory and encourage the employee to find another position.
4.2. The Employment Exit Procedures Used by Two Organizations
One can say that TESCO and ASDA use a similar employment exit procedure that consists of the following stages: review, reference requests, exit interviews, and processing resignation. Both companies use resignation as a way of confirming the last employee's working day. Moreover, the unfinished work can be transferred to another employee, and the line manager becomes responsible for its performance. At the exit interview, the employer and employee can discuss the reasons for leaving. If the employee leaves for personal reasons, the managers can give them a recommendation letter to apply for a new position. Both companies demand that the employees inform them about their exit two weeks before the date of leaving to find another person (Tyler 2013).
4.3. The Impact of the Legal and Regulatory Framework on Employment Cessation Arrangements
The legal and regulatory frameworks have an impact on employment cessation arrangements as they protect employees' rights and guarantee job security. It means that no employee ceases his work without any fair reason. Consequently, the illegal activities of the employer can lead to criminal responsibility (Werner & DeSimone 2012). Any kind of discrimination (ethnic, nationality, race, or gender) is prohibited inside the company. Employees who leave work due to disabilities, pregnancy, or other physical conditions are also protected by the law (Kurup & Rosenbaum 2010).
Conclusion
In conclusion, it becomes evident that HRM is one of the key aspects of the management of the company. In the present times, HRM is more actual and effective than PM as it brings more positive changes in the work with people. First, HRM helps understand the relationship between organizational structure and culture. Second, it applies the different approaches to management and leadership. Third, HRM uses motivational theories in the organizations. Fourth, it implements productive mechanisms for developing effective teamwork


